


Next: 3.19 Detector pixel filter-to-filter
Up: 3. Derive SPD level
Previous: 3.17 Aperture scaling of
3.18 Correction for inhomogeneaous FCS illumination (PHT-C)
synopsis: systematic uncertainty due to residual flat field
uncertainty
limitations and applicability:
possibly dependent on heating power
description:
The non-homogeneous illumination of the arrays by the FCS is corrected for
by using a scale factor for each pixel (illumination matrix). The element
values in the matrix are different for different filters.
purpose correction:
Improves the accuracy of the determination of the individual
detector pixel responsivities.
uncertainty/noise introduced:
The illumination matrices have been determined in orbit. The minimum error
in the determination of the matrices depends on the validity of the
assumption that the illumination matrix is fixed for different FCS
electrical powers. Residual errors in the illumination matrix decrease
the consistency in calibration among the pixels. Table 3
lists the maximum 1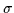 uncertainty for each filter in the array.
uncertainty for each filter in the array.
Table 3:
Maximum uncertainties in the illumination matrix,
plus corresponding pixel
| |
Maximum 1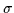 |
|
| filter ID |
uncertainty (%) |
Pixel |
| C_50 |
16 |
1 |
| C_60 |
10 |
9 |
| C_70 |
10 |
3 |
| C_90 |
12 |
5 |
| C_100 |
16 |
1 |
| C_105 |
20 |
7 |
| C_120 |
13 |
3 |
| C_135 |
10 |
3 |
| C_160 |
8 |
3 |
| C_180 |
10 |
1 |
| C_200 |
10 |
3 |
auxillary data:
Cal-G files PC1ILLUM, PC2ILLUM
uncertainties are supplied in the Cal G file.



Next: 3.19 Detector pixel filter-to-filter
Up: 3. Derive SPD level
Previous: 3.17 Aperture scaling of
ISOPHOT Error Budgets: Derive_SPD Processing Steps, Version 1.0, SAI/98-091/Dc