



Next: Search for cool circumstellar
Up: Poster session C Interstellar
Previous: Poster session C Interstellar
A. Abergel 1,
J.P. Bernard 1,
F. Boulanger 1,
J.-L. Puget 1,
M. Gérin 2,
E. Falgarone 2,
L. Nordh 3,
& G. Olofsson 3
1 Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale, Université
Paris-Sud, Bât. 121, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France
2 Radioastronomie Millimétrique, Ecole Normale
Supérieure, Paris, France
3 Stockholm Observatory, S-133 36 Saltsjöbaden, Sweden
The large scale ISOCAM survey of the southern part of Orion B conducted
in the broad-band filters LW2 (5-8.5 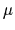 m) and LW3 (12-18
m) and LW3 (12-18 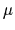 m)
reveals the small scale structure (6'') of the emission in a wide
range of physical conditions and geometry:
m)
reveals the small scale structure (6'') of the emission in a wide
range of physical conditions and geometry:
- The reflection nebula NGC2023 and NGC2024 (southern part)
- The molecular cloud L1630
- The North-South photodissociation region at the western edge of
the molecular cloud
- The HorseHead Nebula which is a dense globule emerging from its
parental cloud due to UV erroding radiations.
Small scale observations of the edge of a cloud illuminated by a
few bright stars allow to strongly constrain the density structure
and the geometry of the cloud. This is spectacularly illustrated
in the HorseHead nebula whose illuminated edge presents one of the
sharpest IR filaments detected by ISOCAM in the interstellar medium.
It gives unprecedented constrains on the geometry and the penetration
of the UV radiations.




Next: Search for cool circumstellar
Up: Poster session C Interstellar
Previous: Poster session C Interstellar
"The Universe as seen by ISO", 20 - 23 October 1998, Paris: Abstract Book