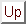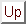


For photometry of point-sources the power on the detector is described by:
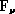 is the flux of the point source in
is the flux of the point source in 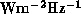 at the
selected wavelength;
at the
selected wavelength;
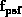 is the fraction of the point spread function which passes
through the aperture and can be found in Tab. 2 and 4.
C1 is a wavelength dependent parameter and is tabulated in Tab. 10.
The following parameters are represented by the factor C1:
is the fraction of the point spread function which passes
through the aperture and can be found in Tab. 2 and 4.
C1 is a wavelength dependent parameter and is tabulated in Tab. 10.
The following parameters are represented by the factor C1:
For extended sources the total power depends on the surface brightness
of the source and the solid angle 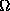 of the aperture, thus:
of the aperture, thus:
where 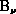 is the flux density of the extended source in
is the flux density of the extended source in
 ,
e is an obscuration factor of the secondary mirror of the ISO telescope,
where
,
e is an obscuration factor of the secondary mirror of the ISO telescope,
where  ,
and
,
and 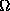 is the solid angle of the aperture or array projected on the sky.
The values for
is the solid angle of the aperture or array projected on the sky.
The values for 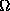 can be found in Tab. 9.
can be found in Tab. 9.
The total noise is described by the following equation:
This includes an additional measurement for background subtraction so that the background and read-out terms are counted twice.
 is the photon noise
for a point source:
is the photon noise
for a point source:
The noise induced by the background 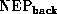 is described by the same
formula, except that
is described by the same
formula, except that 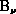 becomes the flux density of the
background:
becomes the flux density of the
background:
 is the detector noise and can be represented by a constant for
each detector:
is the detector noise and can be represented by a constant for
each detector:
PHT03 and PHT22
For chopping observations the observing time on the reference positions has to be added. For rectangular and triangular mode the exposure time is twice the on-source integration time. In saw-tooth mode, where an equal amount of time is spent on the source position and each of the two reference positions, the total exposure time becomes 3 times the on-source integration time.
PHT05 and PHT25
Similar to the AOTs PHT03 and PHT22 in rectangular and triangular chopping mode, the total exposure time is twice the on-source integration time, since the same amount of time is spent on the source and on the FCS.