




Next: 8.3 Common Processing Steps
Up: 8. Data Processing Level:
Previous: 8.1 Overview
Subsections
8.2 PHT Auto Analysis Processing Per AOT
No description is given of the polarisation AOTs PHT50 and PHT51 because
these AOTs are not included in the pipeline SPD and AAR levels.
8.2.1 PHT03
This AOT performs photometry in user-selected wavebands using the PHT-P
subinstrument, with either the staring or chopping mode. If the staring
mode is selected, a raster scan may be performed by the satellite.
The description of the processing required for rasters is incorporated,
since the same steps are required to process measurements at each raster
position.
Processing steps:
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- If single pointing:
- Average source power and off-source background(s) power
- Staring mode
- No action required.
- Chopped mode
- Determine source power, step
8.4.1
- If point source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Write PHT-P point source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.8.
- If extended source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Convert flux density to surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Write PHT-P extended source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.9.
- If raster mapping performed:
- Determine celestial coordinates of detector origin and centre;
loop over all measurements in AOT
Common step 8.3.3;
- For each record, convert power to surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Produce photometric image
Mapping steps 8.5.2 to 8.5.5;
- Write raster map products 8.5.6;
- Write PHT-P raster scan photometry product
Mapping step 8.5.7.
8.2.2 PHT04
This AOT performs multi-aperture photometry with a single user-selected
filter at one sky position using the PHT-P subinstrument. The focal plane
chopper may be operated in either staring or chopping mode. Raster scans may
not be selected.
Processing steps:
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- Average source power and off-source background(s) power
- Staring mode
- No action required.
- Chopped mode
- Determine source power, step
8.4.1
- If point source indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Write PHT-P point source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.8.
- If extended source indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6;
- Convert flux density to surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Write PHT-P extended source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.9.
8.2.3 PHT05
This AOT performs absolute photometry of the sky brightness with a single
filter/aperture combination at one sky position using the PHT-P
subinstrument. Raster scans cannot be selected.
Processing steps:
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- If point source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Write PHT-P point source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.8.
- If extended source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Convert flux density to surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Write PHT-P extended source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.9.
8.2.4 PHT17/18/19
These AOTs perform photometry in user-selected wavebands with a single
user-selected aperture as part of a sparse map using the PHT-P subinstrument.
Only staring mode can be used. The following processing
steps are performed:
Processing steps:
- Loop over all PHT17, PHT18. . ., PHT19 of the same TDT
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- If last product was found then loop over all measurements read:
- If point source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Write PHT-P point source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.8.
- If extended source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Convert flux density to surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Write PHT-P extended source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.9.
8.2.5 PHT22
This AOT performs photometry in user-selected wavebands using the PHT-C
subinstrument, with either the staring or chopping mode. If the staring
mode is selected a raster scan may be performed.
Processing steps:
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- If single pointing:
- Average source power and off-source background(s) power
This step is applied to each pixel.
- Staring mode
- No action required.
- Chopped mode
- Determine source power, step
8.4.1
- Summation of powers in array, step 8.4.2
- If point source was indicated by observer:
- Determine Gaussian parameters
- Interpolation:
- Interpolate missing pixels
Photometry step 8.4.4;
- Fitting:
- Determine source peak and position
Photometry step 8.4.5;
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6;
- Write PHT-C point source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.10.
- If extended source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6;
- Convert flux density to surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Write PHT-C extended source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.11.
- If raster mapping performed:
- Determine celestial coordinates of each detector pixel
for each record;
loop over all measurements
Common step 8.3.3;
- For each record and pixel, convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6;
- For each record and pixel, convert flux density to
surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Produce photometric image
Mapping steps 8.5.1 to 8.5.5;
- Write raster map products
Mapping step 8.5.6.
- Write PHT-C raster scan photometry product
Mapping step 8.5.8.
8.2.6 PHT25
This AOT performs absolute photometry of the sky brightness with a single
filter on one sky position using the PHT-C subinstrument.
Raster scans cannot be selected, only staring mode is available.
Processing steps:
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- If point source was indicated by observer:
- Summation of powers in array, step 8.4.2
- Determine Gaussian parameters
- Interpolation:
- Interpolate missing pixels
Photometry step 8.4.4;
- Fitting:
- Determine source peak and position
Photometry step 8.4.5;
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Write PHT-C point source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.10.
- If extended source was indicated by observer
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Convert flux density to surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Write extended source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.11.
8.2.7 PHT32
This AOT performs multi-filter mapping using either the C100 or C200 arrays.
The map may take the form of a linear scan. A raster scan is performed; the
focal plane chopper being used to sample at intermediate positions from the
raster pointings in sawtooth mode.
Processing steps:
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- Determine celestial coordinates of each detector pixel
for each record;
loop over all measurements
Common step 8.3.3;
- For each record and pixel, convert power to
flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6;
- For each record and pixel, convert flux density to
surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Produce photometric image
Mapping steps 8.5.1 to 8.5.5;
- Write raster map products
Mapping step 8.5.6.
- Write PHT-C raster scan photometry product
Mapping step 8.5.8.
8.2.8 PHT37/38/39
These AOTs perform photometry in user-selected wavebands
as part of a sparse map using the PHT-C subinstrument.
Only staring mode observations are performed.
Processing steps:
- Loop over all PHT37, PHT38. . ., PHT39 of the same TDT
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- If last product was found then loop over all measurements read:
- If point source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Write PHT-C point source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.10.
- If extended source was indicated by observer:
- Convert power to flux density
Photometry step 8.4.6.
- Convert flux density to surface brightness
Photometry step 8.4.7;
- Write PHT-C extended source photometry product
Photometry step 8.4.11.
8.2.9 PHT40
Spectrophotometry with the PHT-S subsystem. Staring, chopped, and mapping
modes are available. Point or extended sources can be observed.
The short (SS) and the long (SL) wavelength detectors are processed
separately.
Processing steps:
- Read SPD Header
Common step 8.3.1.
- Read SPD record
Common step 8.3.2.
- If single pointing:
- If point source was indicated by observer:
- Determine point source spectrum
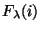 :
step 8.6.1
:
step 8.6.1
- Write point source spectroscopy product
Spectroscopy step 8.6.3.
- If extended source was indicated by observer:
- Determine surface brightness spectrum
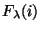 :
step 8.6.2
:
step 8.6.2
- Write extended source spectroscopy product
Spectroscopy step 8.6.3.
- If raster mapping performed:
- Determine celestial coordinates of each raster point:
loop over all raster points in AOT
Common step 8.3.3.
- For each raster point
 ,
determine surface brightness spectrum
,
determine surface brightness spectrum
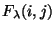 :
:
step 8.6.2.
- Write raster map product:
Spectroscopy step 8.6.3.
For raster observations no images are produced.
For each raster pointing a record containing a spectrum plus the
associated coordinates area are written to the product.





Next: 8.3 Common Processing Steps
Up: 8. Data Processing Level:
Previous: 8.1 Overview
ISO Handbook Volume IV (PHT), Version 2.0.1, SAI/1999-069/Dc